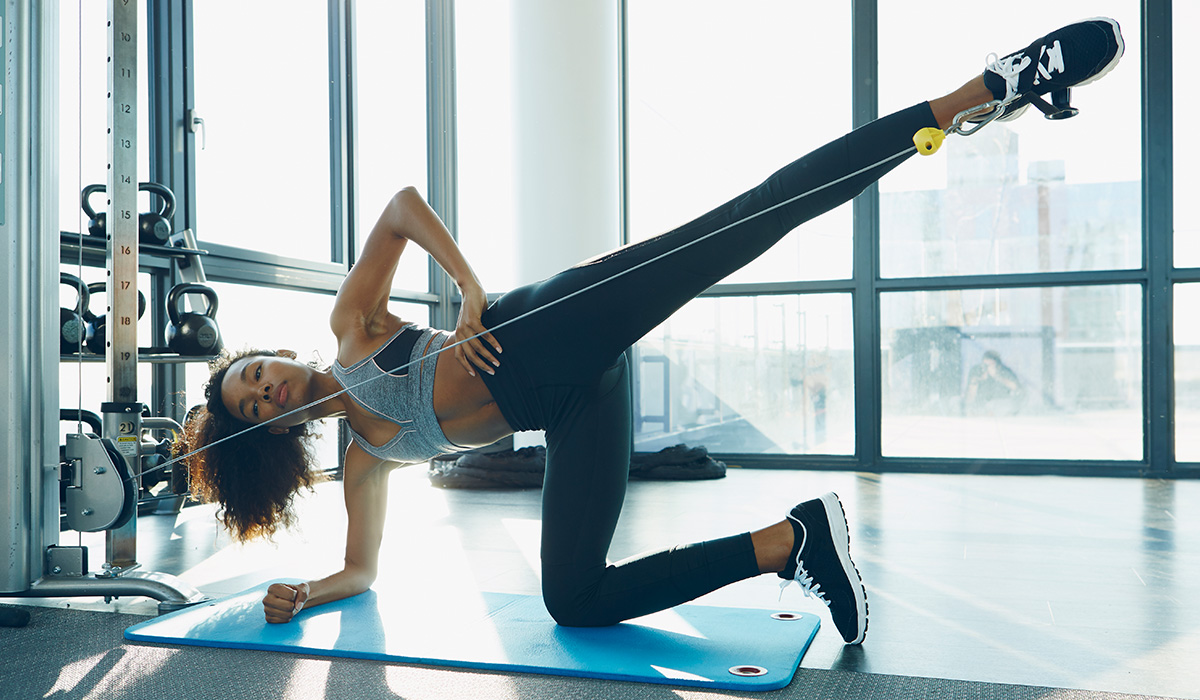
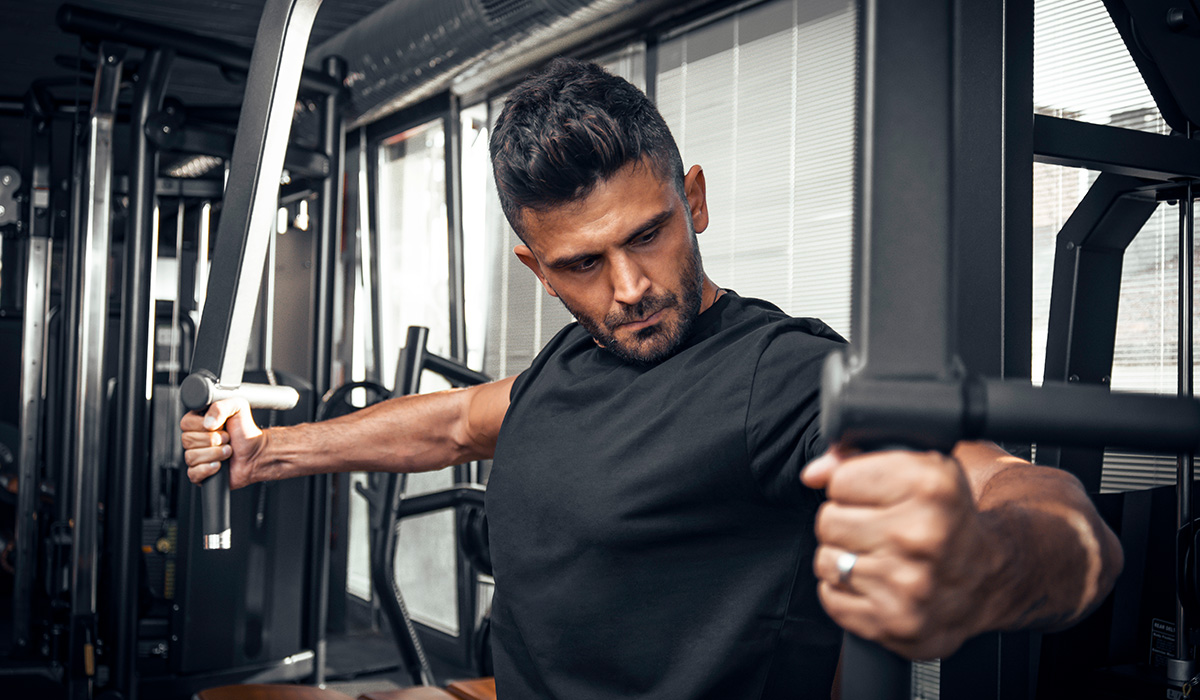
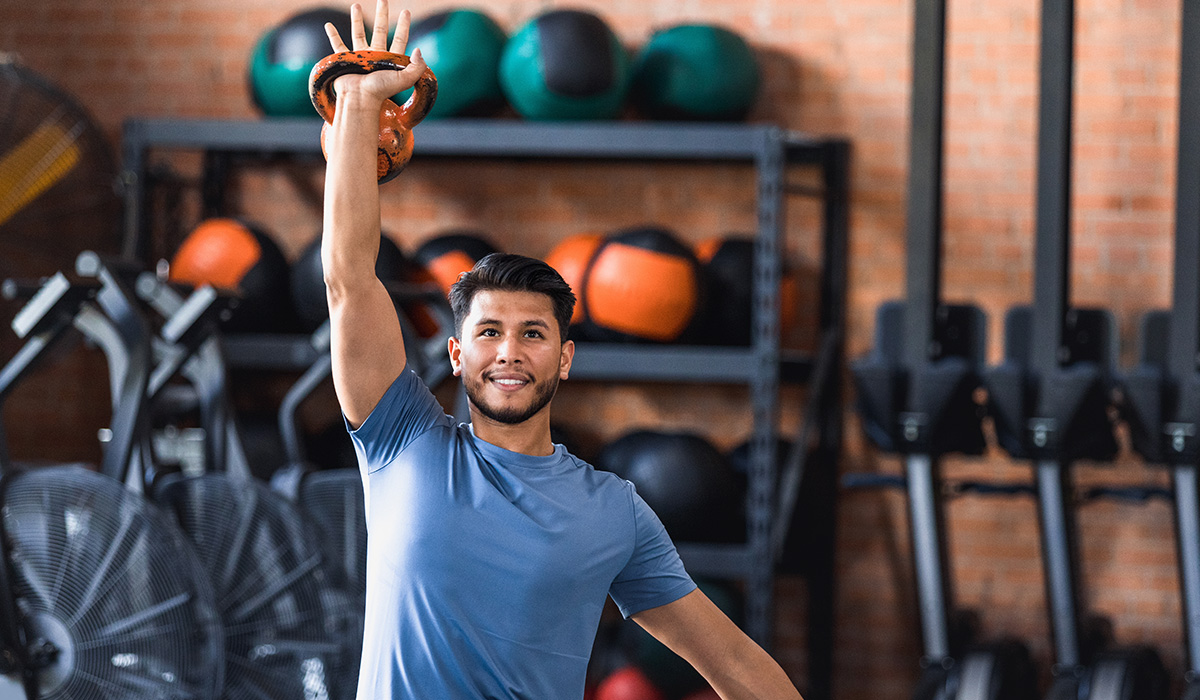
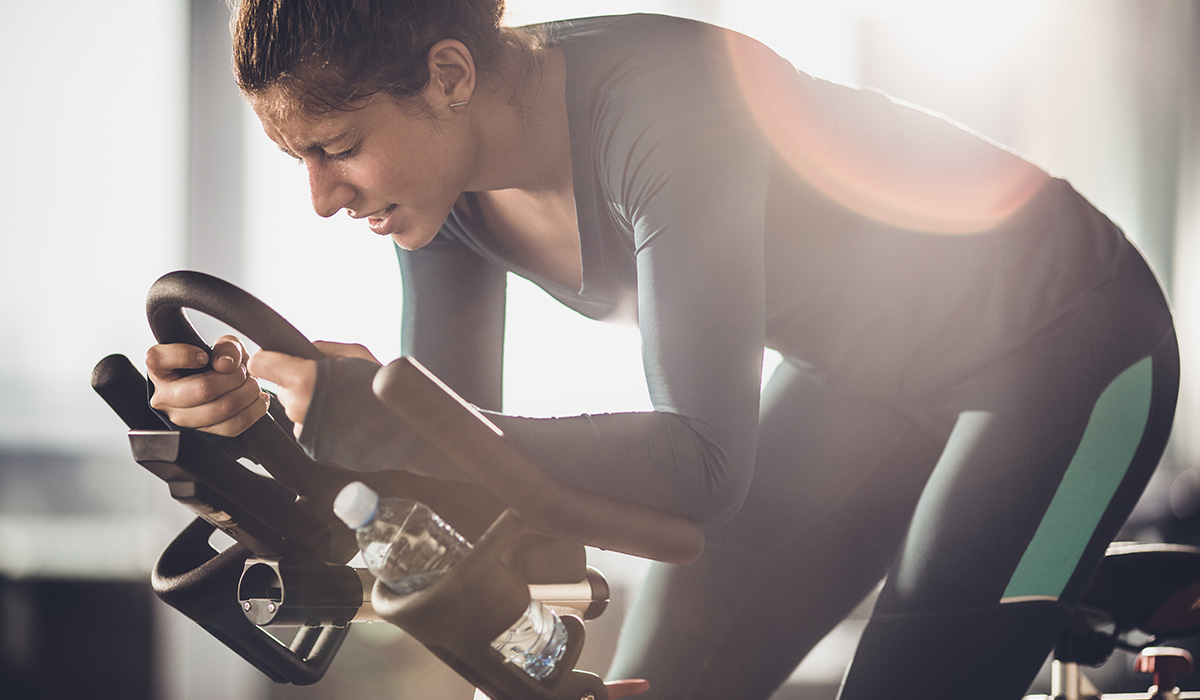
Tri-sets are doing three exercises back-to-back with no break. During these sets you can either pair exercises that are non-competing, in other words opposing muscle groups, or you can target the same muscle. If you are stuck at a training plateau then tri-sets may be what you need to start progressing again!
A tri-set is a series of three exercises performed in a row with 10 second rests between exercises. You could do squats, leg presses and leg extensions for a quadricep tri-set or the bench press, skull crushers and overhead cable extensions for a tricep tri-set
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS?
- Improve muscular endurance and cardiovascular performance
- Increase athletic performance
- Can be time efficient
- Boosts mood and mental health
- Can promote weight loss
- Good for motivation
- Effective for burning calories and building strength